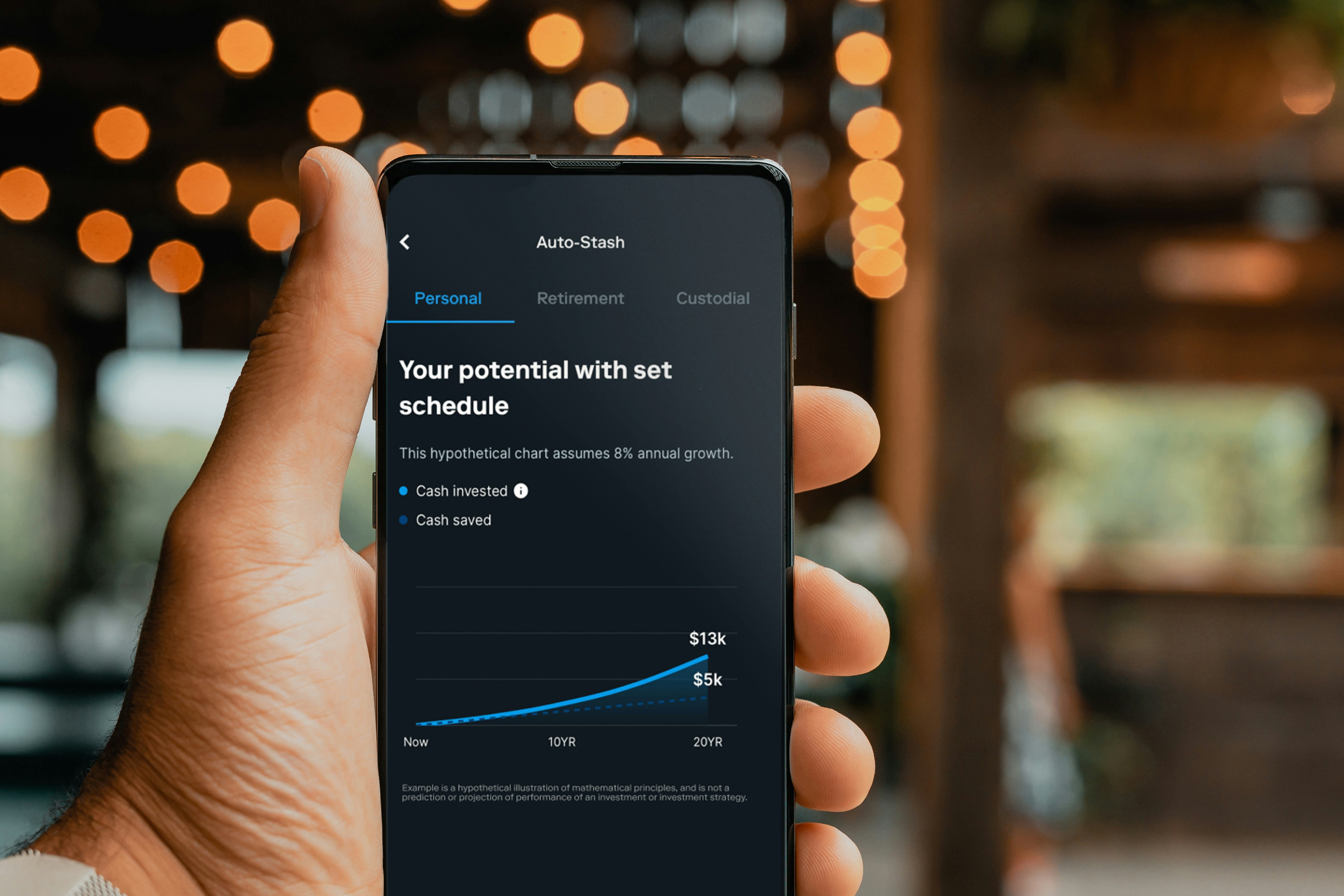
Understanding Personal Finance
Personal finance is a comprehensive term that encompasses various aspects of managing an individual’s financial activities. At its core, personal finance involves practices such as budgeting, saving, investing, and planning for retirement. Each of these components plays a crucial role in achieving financial wellness and stability.
Budgeting is the practice of creating a plan for how to allocate one’s income toward expenses, savings, and investments. By establishing a budget, individuals can track their spending habits, identify areas of potential savings, and ensure they are not living beyond their means. Saving refers to setting aside a portion of income for emergencies, big purchases, or future goals. Typically, a good rule of thumb is to save at least 20% of one’s income. This practice not only provides a financial cushion but also helps individuals gain a sense of security.
Investing, on the other hand, involves using saved money to generate additional income or profit. This can take many forms, including stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and real estate. Understanding the various investment options available is essential for making informed decisions that align with individual financial goals and risk tolerance. Additionally, planning for retirement is vital, as it ensures that individuals can maintain their desired lifestyle after they stop working. This planning includes selecting retirement accounts, understanding contribution limits, and knowing how to manage retirement funds effectively.
The significance of financial literacy cannot be overstated. It empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their finances, ultimately leading to long-term financial stability. Knowledge of key financial terms, such as assets, liabilities, equity, and interest rates, is crucial in navigating personal finance successfully. By grasping these essential concepts, individuals can better manage their finances and work towards achieving their financial goals.
Creating a Personal Budget
Creating a personal budget is a fundamental step toward achieving financial wellness. This process begins with tracking your income and expenses meticulously. By understanding where your money comes from and where it goes, you can identify spending patterns and areas for improvement. Start by listing all sources of income, including salaries, side hustles, and any passive income. Following this, document all fixed and variable expenses, such as rent, utilities, groceries, and entertainment, to gain a comprehensive view of your financial landscape.
Setting financial goals is the next crucial step in the budgeting process. These goals can be short-term, such as saving for a vacation, or long-term, such as planning for retirement. By establishing clear objectives, you will create a roadmap that informs your budgeting decisions. Various budgeting methods can assist in achieving these objectives. The 50/30/20 rule, for example, recommends allocating 50% of your income to needs, 30% to wants, and 20% to savings and debt repayment. Alternatively, zero-based budgeting involves assigning every dollar a specific role, ensuring that all income is accounted for and directed toward expenses or savings.
For those who prefer a more visual approach, the envelope system can be highly effective. This method requires dividing cash into envelopes designated for specific spending categories, helping individuals avoid overspending in any one area. Practical tips for using budgeting tools and apps can further simplify this process. Many applications allow users to input expenses and track progress easily, offering insights and reminders along the way.
Finally, sticking to your budget requires discipline and a willingness to adjust as life circumstances change. Regularly revisiting your budget to reflect changes in income or expenses ensures it continues to meet your needs. Real-life examples demonstrate that effective budgeting not only fosters savings but also paves the way for achieving financial goals and ultimately enhancing financial well-being.
Saving and Investing Wisely
Effective personal finance management requires a balanced approach to both saving and investing. One of the first essentials is the establishment of an emergency fund. This fund acts as a financial safety net, ideally covering three to six months of living expenses. It provides peace of mind and helps individuals navigate unexpected financial challenges without resorting to high-interest debt. To build this fund, individuals should consider setting aside a portion of their income into a dedicated savings account, ensuring that funds remain easily accessible but separate from everyday expenses.
In addition to an emergency fund, it is advisable to set savings goals for both the short and long term. Short-term goals might include saving for a vacation or a new appliance, while long-term objectives could focus on retirement or a child’s education. Different types of savings accounts can help in this regard, including high-yield savings accounts for short-term needs and certificates of deposit (CDs) for longer commitments, which typically offer higher interest rates in exchange for locking in funds for a fixed period.
Once saving strategies are in place, attention can turn to investing. Understanding the various investment vehicles is crucial. Stocks represent ownership in a company and can potentially offer high returns, while bonds are loans made to corporations or governments that yield fixed interest over time. Mutual funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are popular options for diversifying investments, pooling money from multiple investors to purchase a diversified portfolio of assets.
As individuals delve into the world of investing, it is vital to grasp the principles of risk and return. Generally, higher potential returns are associated with higher risk. This relationship highlights the importance of assessing personal risk tolerance before making investment decisions. Finally, the power of compound interest cannot be overstated; by starting to invest early, individuals can significantly increase their wealth over time, as their investments grow on both initial contributions and accumulated interest.
Planning for Retirement and Beyond
Planning for retirement is an essential component of achieving long-term financial wellness. It requires a comprehensive strategy that accounts for various factors, including lifestyle goals, healthcare costs, and potential income sources. One primary tool for retirement savings is the 401(k), often provided through employers. This type of account allows employees to contribute a portion of their salary on a pre-tax basis, reducing their taxable income while saving for the future. Additionally, many employers offer matching contributions, which can significantly increase retirement savings over time.
Another popular retirement account is the Individual Retirement Account (IRA), which comes in several variations, including traditional and Roth IRAs. A traditional IRA allows for contributions to be tax-deductible, but taxes are due upon withdrawal during retirement. Conversely, a Roth IRA features tax-free growth, as contributions are made with after-tax income, allowing for tax-free withdrawals in retirement. Understanding the tax implications of these accounts is key to making informed decisions about which is best suited for one’s financial situation.
Establishing a retirement savings strategy involves calculating how much money one needs to retire comfortably. Factors to consider include expected retirement age, desired lifestyle, and other income streams, such as Social Security or pensions. Financial advisors often recommend targeting a retirement income that replaces around 70% to 80% of pre-retirement earnings, adjusted for inflation.
Moreover, estate planning is a crucial aspect of financial wellness as individuals approach retirement. Creating a will ensures that assets are distributed according to one’s wishes, while establishing trusts may offer additional control over how assets are managed and distributed. It is advisable to engage in discussions about financial matters with family members, aiding in a smooth transition of assets and mitigating potential disputes. By proactively planning for retirement and addressing estate concerns, individuals can secure their financial future and provide peace of mind for their loved ones.